5th Metatarsal Stress Fracture Treatment & Management
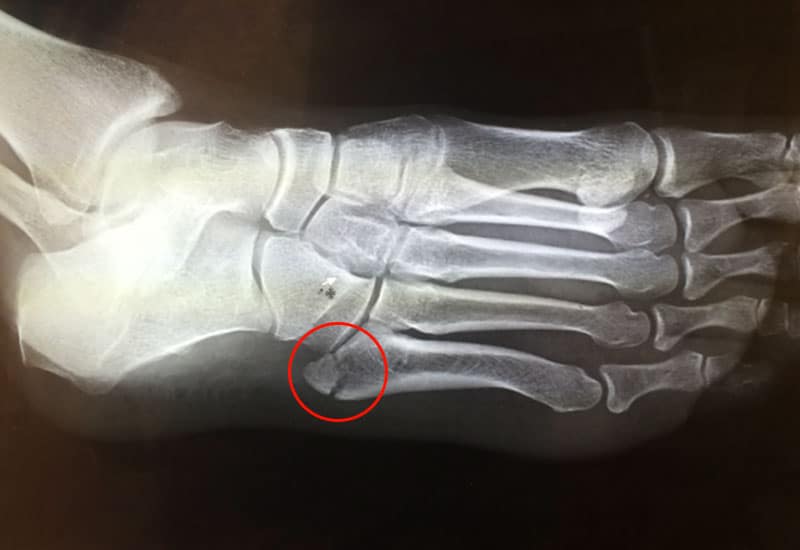
See attached, this image shows a fracture of the 5th meta tarsal.
A stress fracture is also called as Hairline fracture and is a fracture of the bone caused by the repeated stress. As a result of accumulated trauma from submaximal loadings like jumping and running a fracture is caused instead by a single severe impact. In athletes, stress fractures are overuse injuries because of the mechanism.
A small crack in the bone will be called as a stress fracture and are mostly common to us as Hairline fracture. They occur in weight-bearing bones such as the metatarsals, navicular bones, and tibia. Femur, sacrum, and pelvis will not have much stress like the others and are safe from stress fractures.
Symptoms and signs:
Usually, the pain with weight bearing is increased when involved in various activities and exercises. On taking rest, the pain subsides but can lead to a more serious bone injury later on. Swelling will be present on the area where there is a crack on the bone. Palpation and percussion on the bones produce symptoms.
Diagnosis:
Doctors prefer MRI, CT, or 3-phase bone scan for an effective diagnosing. X-rays cannot always show the evidence of stress fractures but can be used when the bone retains its strength.
Causes:
Bones will try to repair and remodel themselves especially when extraordinary stress is applied. If more stress is applied to the bones, there is a chance for the bones to get weaker and exhausts the capacity of the bones to remodel. This does not appear all of a sudden but occurs from repeated trauma and develop a condition in which there can be a sudden break.
Sedentary people experience this kind of stress fractures and can also occur in athletes while completing their high impact training, and high volume such as jumping and running sports. Soldiers too experience hairline fractures as they have long distances to march.
Prevention:
Adding more stress to your bones is one way to avoid stress fractures. You might think I was being funny as these stress fractures are mainly caused due to the high stress on bones. But you should keep in mind that to apply moderate stress to the bones in a controlled manner. This can increase the strength of the bones and they become less susceptible to a fracture.
Some of the exercises which increase strength will also help to avoid a crack on the bones. The daily exercise is good for the body and the strengthened muscles will prevent the bones from becoming fatigued.
Treatment:
Rest is the best option to heal the fracture. The time required for the recovery will depend on upon the severity, location and also the strength of the body response to healing the fracture. A period of 4 to 8 weeks should be given for rest and walking boots are preferred during this period.
Rehabilitation is a training to strengthen the muscles and will help to dissipate the force being transmitted on the bones.
Rehabilitation, in this case, will take a time period of about 6 months.








