Do you have Flat Feet? This happens with Adults and Children
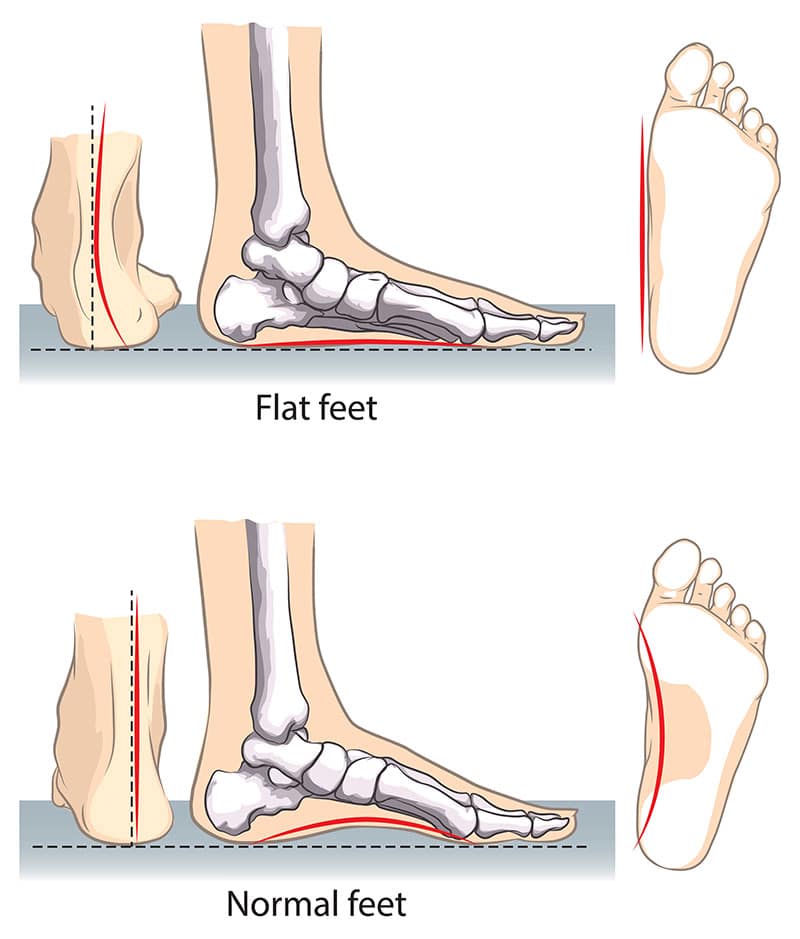
Flat feet is defined as a postural superiority where the arches of the foot tend to collapse and the entire sole comes into complete contact with the ground. Some individuals have an arch of the foot in which it never develops in just one foot or both. A functional relationship exists between the biomechanics of lower leg and structure of arch of the foot. The arch provides a springy and elastic connection between the hindfoot and forefoot. The association moves forward by safeguarding as the majority of forces incurred during the weight bearing of the legs which will be dissipated before the long bones of thighs and legs experience the force associated with it.
The head of the talus bone, known as pes planus is distal from navicular and displaced medially. The tibialis posterior muscle tendons and the spring ligament gets stretched and so the individual with pes planus would lose the function of the MLA (medial longitudinal arch). The individual will have a rigid flatfoot if the MLA is nonfunctional or absent in both standings and in seated positions. If in case the MLA is functional and present while the individual is standing or sitting up on the toes, the person will tend to have a flexible flatfoot. Well-fitting arch supports will be used to correct this latter condition. The flat foot can be caused in children as well as for adults.
Children:
In infants, the appearance of the flat feet is quite common and normal which is due to the baby fat that masks the developing arch. In early childhood and infancy, the growth of human arch is very common and is a part of normal, tendon, muscle, bone growth and ligament. Walking barefoot on different terrain and foot training, especially the foot gymnastics will facilitate the formation and increase the growth of arches during childhood. The developed arch occurs by the end of 6 years to the maximum. Hypermobility and dyspraxia are some of the genetic musculoskeletal conditions which are considered as symptoms for flat feet.
Ligament laxity is one of the factors associated with flat foot and so the shoe-wearing children associated with ligament laxity have a greater chance of developing arches compared to other shoe wearing children. The children who walk barefoot will also have an increased chance of developing more human arches. So instead of using flip flops and sandals, it is better to use closed-toe shoes.
Adults:
Development of flat foot is common in adults due to illness, injury, prolonged or unusual stress to the foot, a fault in biomechanics, and also increases the chances with age. Women of over 40 years will experience flat foot and is common among them. The risk factors which increase the chances of developing arches after a certain age are diabetes, hypertension, and obesity.
Most flat feet do not cause pain and are asymptomatic. Flat feet was a physical health reason for rejecting services in the military. Treatment must be done if there is a pain anywhere in the lower leg, lower back and the knees. Treatment is done using orthoses which include foot gymnastics, arch support or other exercises which are recommended by a physical therapist.








